





THE BENEFICIAL EFFECTS OF EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY ARE WIDELY KNOWN. SCIENTISTS RECOGNIZE THAT SHOCKWAVES CAN TRIGGER A VARIETY OF EFFECTIVE ACTIONS RELEASES MORE SUBSTANCE P > One of these messenger substances is substance P, a pain mediator and growth factor. On the one hand, the release of substance P by shockwaves has an analgesic effect. On the other, it dilates the blood vessels, stimulates blood circulation and contributes to the formation of new bone tissue. NO (nitric oxide) also has a vasodilatory effect and plays an important role in angiogenesis. > In short, when applied where pain occurs, we know why shockwaves produce an analgesic effect, increase blood circulation and facilitate the repair process. INHIBITS THE COX II ENZYME > By inhibiting inflammatory mediators such as COX II, shockwaves produce an anti-inflammatory effect. This weakens any inflammatory process. ACTIVATES CELLULAR DEFENSES > By contributing to the release of free radicals, shockwaves help strengthen the body’s endogenous cellular defense mechanisms to protect it from disease. HYPERSTIMULATES NERVE FIBRES > Scientific studies also show that shockwaves act in another way. Overstimulating the nerve fibres blocks an increase in pain stimuli and therefore intensifies the analgesic effect (Gate Control Theory). |
HOW SHOCKWAVES AND
TISSUES INTERACT DURING THERAPY
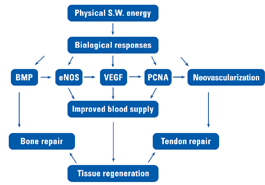
ACCELERATED TISSUE REPAIR AND CELL GROWTH
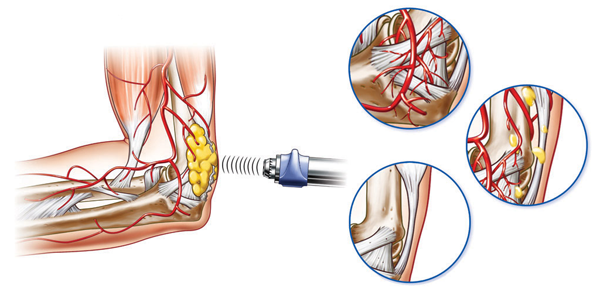
Ingrowth of Neovascularization
Nutrient blood flow is necessary to start and maintain the repair processes of damaged tissue structure. The application of acoustic waves creates capillary micro-ruptures in tendon and bone and significantly increasing the expression of growth indicators such as the eNOS, VEGF, PCNA and BMP.
These two processes stimulate the growth and remodeling of new arterioles. The new blood vessels will improve the blood supply and the oxygenation resulting in the faster healing of both tendon and bone.
Reversal of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation occurs when the inflammation response is not completely halted. It can damage healthy areas in the body and can result in chronic pain. The activity of mast cells, which are involved in inflammatory process, may be increased by pervasive acoustic waves.
Mast cell activation may be followed by the synthesis of chemokines and cytokines. The releasing of pro-inflammatory compounds, when needed, may help to restore the normal healing and regenerative processes
.
Stimulation of Collagen
The production of sufficient amounts of collagen is a necessary precondition of the tissue repair process. Shockwave therapy hastens procollagen synthesis. The newly created collagen fibers are forced into a longitudinal structure. These newly formed tendon fibers are more dense and stiff.
ANALGESIA AND MOBILITY RESTORATION
Dispersion of Pain Mediator “Substance P”
Substance P is neurotransmitter that mediates pain information through the C-fibers. This neuropeptide is generally associated with intense, persistent and chronic pain. It is used to relay pain messages to the central nervous system. Lowering the concentration of Substance P reduces the stimulation of afferent nociceptive fibers and thus reduces the pain. Decreasing Substance P, histamines and other nociceptive metabolites also help to inhibit development of inflammatory oedema.
Plantar Fasciitis:
Is commonly found in athletes, overweight individuals, and people whose career or lifestyle has them standing on their feet, or hard surfaces for extended periods of time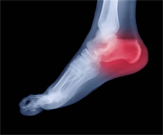
The condition is most often seen in middle-aged men and women, but is found in all age groups. It can affect people with high arches, normal arches, and flat feet. Other factors such as foot pronation, poor fitting shoes, previous trauma, occupational hazards, or even a change in your workout can initiate Plantar Fasciitis.
Over 2 million people suffer from Plantar Fasciitis . Many of these cases are resolved with simple, conservative measures or lifestyle changes that reduce irritation and pain.
Prior to being treated with ESWT, patients must have been diagnosed with chronic Plantar Fasciitis . Only after a patient's symptoms fail to respond to conservative treatments should ESWT be administered. These conservative treatments can include injections, night splints, heal cushions, orthotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, In the past, surgery was the only option available when conservative measures didn't work. Today, non-invasive ESWT offers an alternative to surgery and successful relief from chronic pain.
The Swiss DolorClast® Method is intended to be used by patients who are 18 years of age or older who have symptoms of chronic Plantar Fasciitis that have tried other conservative therapies without success.

